Transformers are pivotal components in electrical power networks, ensuring efficient voltage regulation and electrical isolation. One of the most vital aspects of transformer maintenance and commissioning is the core insulation test. This procedure assesses the integrity of the insulation between the transformer’s core and earth, directly impacting both operational safety and equipment longevity.
What is a Core Insulation Test?
A core insulation test evaluates the insulation resistance between the transformer core (including the clamps or structural steel parts attached to it) and the earth (ground). The purpose is to ensure there is no unwanted electrical leakage path, which can cause heating, faults, or even catastrophic transformer failures.

Why is the Core Insulation Test Important?
- Prevents Electrical Faults: Detects degradation or breakdown of insulation before the transformer is energized in service.
- Ensures Operational Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents due to insulation failure, protecting both personnel and equipment.
- Monitors Transformer Health: Provides early warning of insulation aging, deformation, or contamination from moisture and dust.
When Should the Test Be Conducted?
- During initial installation and commissioning of a transformer.
- As part of routine preventive maintenance schedules.
- After major faults, repairs, or extended periods of storage or inactivity.
How is the Core Insulation Test Performed?
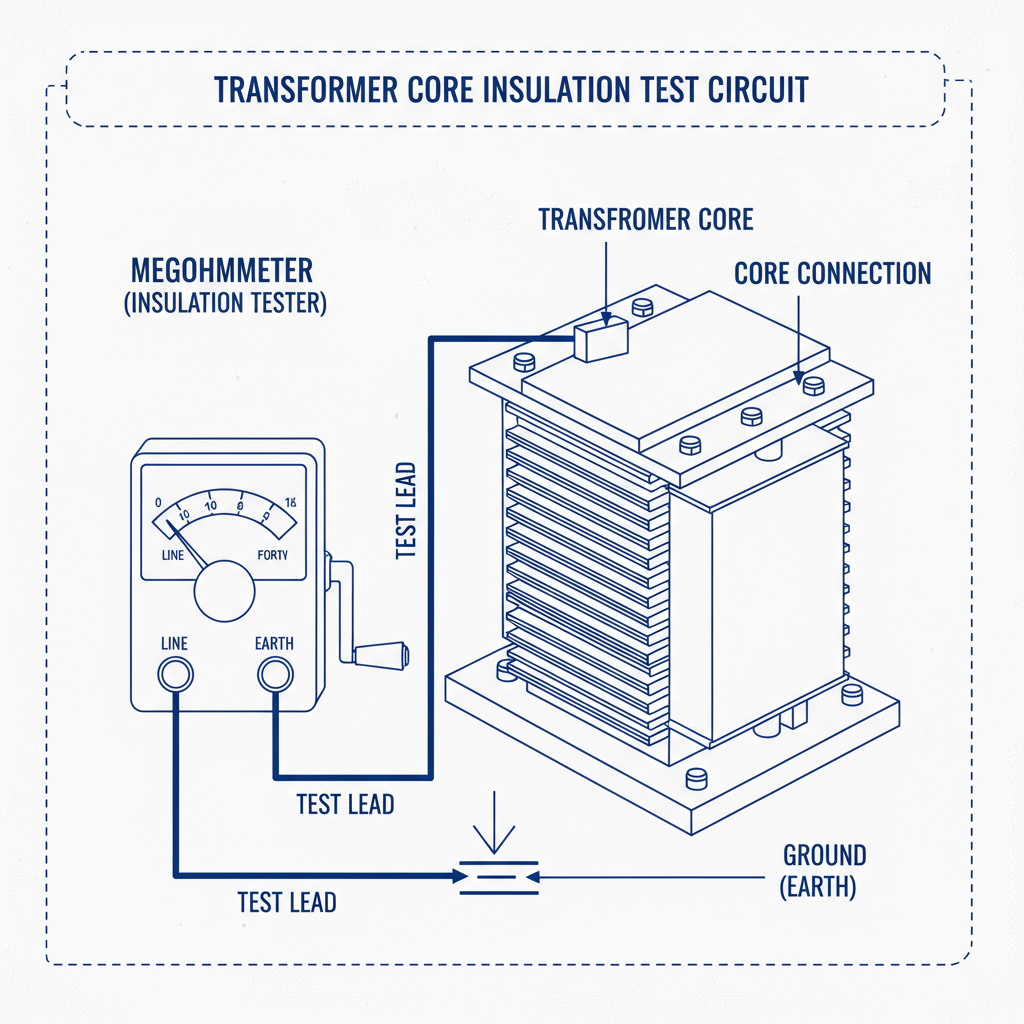
Steps Involved
- Preparation:
- De-energize the transformer and ensure all windings are properly grounded.
- Disconnect any core earthing connection, except for the terminal under test.
- Equipment Needed:
- Use a high-quality insulation resistance tester (commonly called a megohmmeter).
- Testing Procedure:
- Connect the tester’s one lead to the transformer core (usually at the core earth terminal).
- Connect the other lead to the transformer tank (earth).
- Apply the recommended DC test voltage (generally 1,000V or higher for power transformers).
- Record the insulation resistance reading, typically in Megaohms (MΩ).
- Duration:
- Maintain the test voltage for 1 minute to allow for charge stabilization and absorption current.
- Restore Core Earth:
- After completion, ensure the core is properly re-earthed.
Typical Results
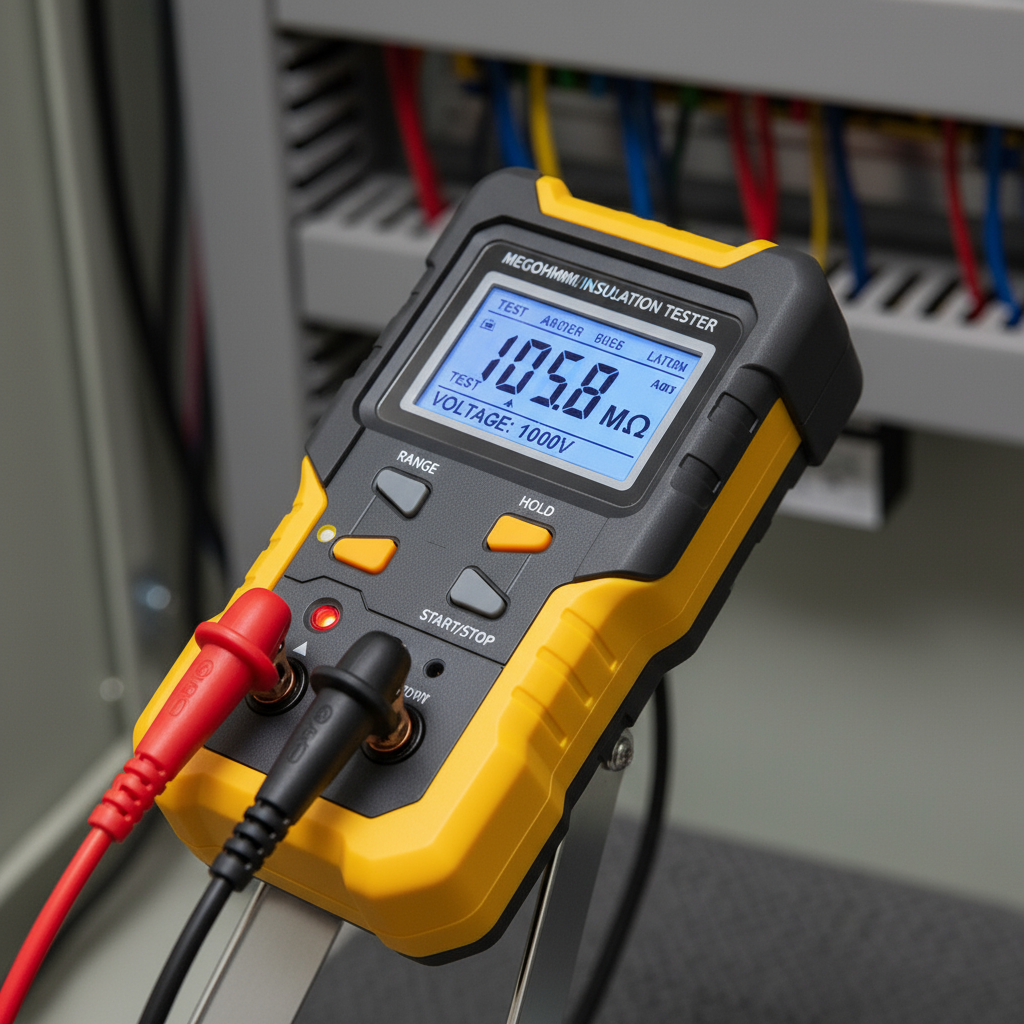

- Healthy transformers generally exhibit insulation resistance in the range of hundreds to thousands of Megaohms, depending on their size, age, and service conditions.
- Low or decreasing readings may signal contaminated, aged, or damaged insulation, requiring further investigation or remedial measures.
Best Practices and Safety Tips
- Always follow proper lockout-tagout (LOTO) procedures before performing any electrical test.
- Monitor environmental conditions—humid or contaminated environments can significantly affect readings.
- Use only calibrated and properly functioning test equipment.
- Never leave the core unearthed after testing is completed.
Common Causes for Low Insulation Resistance
- Presence of moisture due to water ingress or condensation
- Accumulation of dust, oil, or other conductive contaminants
- Mechanical damage or aging of insulation materials
- Inadequate or loosened core earth connections
Conclusion
The core insulation test is an essential part of transformer maintenance and commissioning. By verifying the insulation integrity between the core and earth, electrical engineers can significantly enhance the safety, reliability, and performance of transformer operations. Regular testing, combined with proper maintenance, ensures that transformers operate effectively and trouble-free for years.