Voltage regulation stands as one of the most critical performance indicators in transformer design and operation. This fundamental parameter is essential for electrical engineers involved in power system design, transformer selection, and electrical distribution network optimization. This blog post explains the theoretical foundations, mathematical formulations, practical implications, and real-world applications of transformer voltage regulation.
Definition of Voltage Regulation and Its Significance
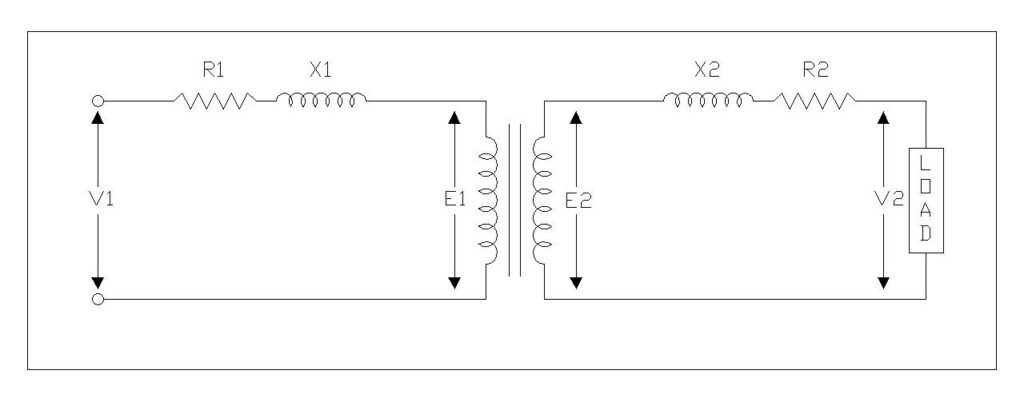
Voltage regulation of a transformer represents the change in secondary terminal voltage that occurs when the load varies from no-load to full-load conditions while the primary voltage remains constant. This parameter quantifies a transformer’s ability to maintain stable output voltage despite variations in load demand.
When a transformer operates under no-load conditions with its secondary terminals open-circuited, minimal current flows through the windings, resulting in negligible voltage drops across the internal impedance. However, as load increases and current flows through both primary and secondary windings, voltage drops develop across the winding resistance and leakage reactance. These voltage drops cause the secondary terminal voltage to decrease from its no-load value, and this variation constitutes the voltage regulation of the transformer.
The fundamental importance of voltage regulation stems from several critical factors.
First, it directly impacts the performance and lifespan of electrical equipment connected to the transformer’s secondary side. Sensitive electronic devices, industrial machinery, and precision instruments require stable voltage supplies to function correctly. Excessive voltage fluctuations can lead to equipment malfunction, reduced efficiency, accelerated aging, and in severe cases, permanent damage to connected loads.
Second, voltage regulation serves as an indicator of transformer design quality and internal losses. Transformers with lower voltage regulation values demonstrate superior design characteristics, minimal internal impedance, and better overall efficiency.
Third, voltage regulation compliance is mandated by national and international standards governing transformer manufacturing and power system operation.
Basic Voltage Regulation Formula
The voltage regulation of a transformer is mathematically expressed as the percentage change in secondary voltage from no-load to full-load conditions.
The standard formula is given by:
\( Voltage \, Regulation (\%) = \frac{E_2 – V_2}{E_2} \times 100 \)
where, \(E_2\) represents the secondary terminal voltage at no-load, and \(V_2\) denotes the secondary terminal voltage at full-load.
Alternatively, this can be expressed in terms of primary winding parameters as:
\( Voltage\, Regulation (\%) = \frac{E_1 – V_1}{E_1} \times 100 \)
where \(E_1\) is the no-load primary terminal voltage and \(V_1\) is the full-load primary terminal voltage.
The ideal transformer would exhibit zero voltage regulation, meaning the secondary voltage remains constant regardless of load variations. However, real transformers always possess finite internal impedance comprising winding resistance and leakage reactance, which inevitably causes voltage drops under load. Therefore, practical transformers always exhibit some degree of voltage regulation, and the design objective is to minimize this value to achieve better performance.
Voltage Regulation and Power Factor
The voltage regulation formula becomes more sophisticated when accounting for the power factor of the connected load. The approximate expression for voltage regulation considering load power factor is:
\( VR = \frac{I_2 R_{02} \cos\phi_2 \, \pm \, I_2 X_{02} \sin\phi_2}{E_2} \)
where \(I_2\) represents the secondary load current, \(R_{02}\) is the equivalent secondary resistance, \(X_{02}\) is the equivalent secondary reactance, and \(\phi_2\) is the power factor angle.
This can also be expressed in per-unit or percentage form as:
\( VR (\%) = R_{pu} \cos\phi \,\pm\, X_{pu} \sin\phi \)
where \(R_{pu}\) and \(X_{pu}\) are the per-unit resistance and reactance respectively. The critical aspect of this formula is the sign convention: the positive sign applies to lagging (inductive) power factors, while the negative sign applies to leading (capacitive) power factors.
Power Factor Effects on Voltage Regulation
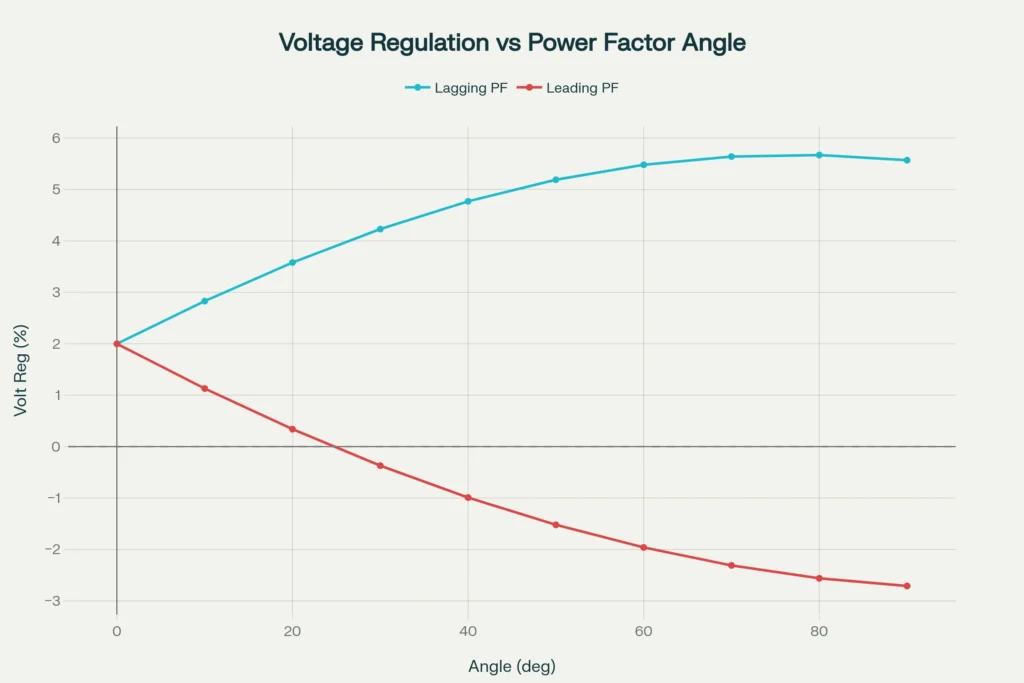
The power factor of the connected load exerts profound influence on transformer voltage regulation, and understanding these effects is crucial for power system design. The relationship between power factor and voltage regulation can be categorized into three distinct cases based on load characteristics.
Lagging Power Factor (Inductive Loads)
When a transformer supplies inductive loads such as motors, induction furnaces, or fluorescent lighting ballasts, the load current lags behind the voltage by an angle \(\phi\). For lagging power factor conditions, the voltage regulation formula becomes:
\( VR = R \cos\phi + X \sin\phi \)
Both resistance and reactance voltage drops contribute additively to the total voltage regulation, resulting in positive and relatively high regulation values.
The secondary terminal voltage decreases significantly as load increases, which represents poor voltage regulation performance. Industrial facilities with predominantly inductive loads often experience substantial voltage drops during peak demand periods, necessitating voltage regulation equipment or power factor correction measures.
Leading Power Factor (Capacitive Loads)
Capacitive loads, including synchronous condensers, power factor correction capacitors, and certain electronic power supplies, cause the load current to lead the voltage. For leading power factor conditions, the voltage regulation expression becomes:
\( VR = R \cos\phi – X \sin\phi \)
The negative sign indicates that the reactive voltage drop across the leakage reactance opposes the resistive voltage drop. This opposition can result in negative voltage regulation, meaning the full-load secondary voltage actually exceeds the no-load voltage. This phenomenon, while seemingly counterintuitive, occurs because the capacitive load current creates a voltage rise across the transformer’s leakage reactance that more than compensates for the resistive voltage drop.
Unity Power Factor (Resistive Loads)
For purely resistive loads such as incandescent lighting and heating elements, the power factor equals unity (\(cos\phi=1\), \(\sin\phi=0\)). The voltage regulation simplifies to:
\( VR = R \cos\phi = R \)
At unity power factor, only the resistive voltage drop contributes to regulation, as there is no reactive component. This typically results in moderate voltage regulation values between those observed for lagging and leading power factors.
Zero and Maximum Voltage Regulation Conditions
Achieving Zero Voltage Regulation
Zero voltage regulation represents an ideal operating condition where the full-load and no-load secondary voltages are equal. This condition can be theoretically achieved at a specific leading power factor where the resistive and reactive voltage drops exactly cancel each other.
For zero voltage regulation to occur, the following condition must be satisfied:
\( R \cos\phi = X \sin\phi \)
Rearranging this expression yields:
\( \tan\phi = \frac{R}{X} \)
Therefore, the power factor angle at which zero regulation occurs is:
\( \phi = \arctan\left(\frac{R}{X}\right) \)
And the corresponding power factor (leading) is:
\( \cos\phi = \frac{X}{\sqrt{R^2 + X^2}} = \frac{X}{Z} \)
The negative sign in the tangent relationship indicates that this power factor must be leading (capacitive load). At power factors more leading than this critical value, the voltage regulation becomes negative, meaning the full-load voltage exceeds the no-load voltage. This principle is sometimes exploited in power systems to maintain voltage stability under varying load conditions, particularly in long transmission lines where capacitive compensation is required.
Maximum Voltage Regulation
Maximum voltage regulation occurs when the load is purely inductive, with a power factor approaching zero lagging. Under this extreme condition, the current lags the voltage by approximately 90 degrees (\(cos\phi\approx 0\), \(ain\phi\approx 1\)). The voltage regulation formula reduces to:
\( VR_{max} \approx X \)
This represents the worst-case scenario for voltage regulation, as the entire reactive voltage drop contributes to the regulation with minimal offsetting from the resistive component.
Practical Calculation Examples
To illustrate the practical application of voltage regulation concepts, consider several representative examples encountered in electrical engineering practice.
Example 1: A single-phase transformer exhibits a no-load secondary voltage of 240 volts and a full-load secondary voltage of 230 volts. The voltage regulation is calculated as:
\( VR (\%) = \frac{240 – 230}{240} \times 100 = 4.17\% \)
This 4.17% regulation indicates that the secondary voltage drops by approximately 10 volts (4.17% of 240V) when transitioning from no-load to full-load operation.
Example 2: A transformer with 2% equivalent resistance and 5% equivalent reactance operates at full load with 0.8 lagging power factor. The voltage regulation is:
\( VR (\%) = 2 \times 0.8 + 5 \times 0.6 = 1.6 + 3.0 = 4.6\% \)
If the same transformer supplies a 0.8 leading power factor load:
\( VR (\%) = 2 \times 0.8 – 5 \times 0.6 = 1.6 – 3.0 = -1.4\% \)
The negative value indicates the full-load voltage exceeds the no-load voltage by 1.4%.
Example 3: A transformer with 5% voltage regulation delivers 115.5 volts at full load. The no-load voltage can be determined by rearranging the regulation formula:
\( 5\% = \frac{E_2 – 115.5}{115.5} \times 100 \)
Solving for \(E_2\):
\( E_2 = 115.5 + 115.5 \times 0.05 = 121.275 \,volts \)
Factors Influencing Voltage Regulation
Multiple interrelated factors determine the voltage regulation characteristics of a transformer. Some of them are detailed below:
1. Transformer Internal Impedance
The internal impedance of a transformer, comprising winding resistance and leakage reactance, constitutes the primary determinant of voltage regulation. Higher impedance values produce greater voltage drops under load, resulting in poorer voltage regulation. The winding resistance depends on conductor material (typically copper or aluminum), conductor cross-sectional area, winding length, and operating temperature. Leakage reactance arises from magnetic flux that links only one winding without linking the other, and it depends on winding geometry, core configuration, and the physical spacing between primary and secondary windings.
Transformer designers can minimize internal impedance through several approaches: using larger conductor sizes to reduce resistance, optimizing winding configurations to minimize leakage flux, employing interleaved or sandwich winding arrangements to enhance magnetic coupling, and selecting high-quality core materials with superior magnetic properties.
2. Load Magnitude and Characteristics
The magnitude of the connected load directly influences voltage regulation through its effect on winding currents and consequent voltage drops. As load current increases from zero to rated value, the voltage drops across internal impedance grow proportionally, causing progressive deterioration in voltage regulation. Heavy loads produce more pronounced voltage drops and higher regulation percentages compared to light loads.
Load characteristics, including power factor and harmonic content, significantly impact voltage regulation performance. Inductive loads impose higher regulation penalties compared to resistive or capacitive loads of equivalent power rating. Non-linear loads generating harmonic currents can cause additional voltage distortion and apparent voltage regulation beyond that predicted by fundamental frequency analysis.
3. Transformer Design and Construction
Fundamental design choices during transformer development profoundly affect voltage regulation characteristics. Core material selection influences both core losses and magnetic properties affecting leakage reactance. Modern grain-oriented electrical steel and amorphous metal cores offer superior performance compared to conventional materials. Winding configuration choices—including layer-type versus disc-type windings, winding arrangement (concentric or interleaved), and tap changer implementation—all impact voltage regulation.
4. Operating Conditions
Environmental factors and operating conditions affect voltage regulation through their influence on winding resistance and magnetic properties. Temperature variations alter conductor resistance according to the positive temperature coefficient of metals. A transformer operating at elevated temperatures exhibits higher winding resistance compared to operation at ambient temperature, resulting in increased voltage regulation. Ambient temperature, cooling system effectiveness, and loading history all contribute to the thermal operating point and consequent resistance values.
Methods to Improve Voltage Regulation
Several practical techniques exist for improving voltage regulation in transformers and power distribution systems, each suited to specific applications and operating conditions.
1. Tap Changing Mechanisms
Tap changers represent one of the most widely employed methods for voltage regulation in power transformers. Tap changers modify the transformer turns ratio by connecting to different points (taps) on the transformer winding, thereby adjusting the voltage transformation ratio to compensate for variations in supply voltage or load conditions.
Off-load tap changers (OLTCs) require the transformer to be de-energized before tap position changes, making them suitable for applications with infrequent voltage adjustments. These devices are commonly found in distribution transformers serving relatively stable loads. On-load tap changers (OLTCs or LTCs) enable tap changes while the transformer remains energized and supplying load.
2. Reactive Power Compensation
Installing shunt capacitor banks provides reactive power compensation that improves system power factor and reduces voltage regulation issues. Capacitors supply reactive power locally, reducing the reactive current flowing through transformer impedance and consequently decreasing voltage drops.
Series capacitors, though less common, compensate for the inductive reactance of transmission lines and transformer leakage reactance, effectively reducing the total system impedance. This technique finds application in long transmission lines and high-voltage power systems requiring voltage regulation improvement.
3. Voltage Regulators
Dedicated voltage regulator devices, including automatic voltage regulators (AVRs) and static var compensators (SVCs), provide dynamic voltage regulation capabilities. AVRs continuously monitor voltage and adjust their output through electronic control or electromechanical mechanisms to maintain stable voltage regardless of input variations or load changes. These devices offer faster response times compared to mechanical tap changers and can provide more precise voltage control.
Static var compensators employ power electronic devices to inject or absorb reactive power dynamically, providing rapid voltage regulation and power factor correction. Advanced FACTS (Flexible AC Transmission System) devices including STATCOMs (Static Synchronous Compensators) offer even more sophisticated voltage control capabilities for critical applications.
4. System Design Optimization
Fundamental system design choices significantly impact voltage regulation performance. Selecting appropriately sized transformers with adequate capacity prevents excessive loading that exacerbates voltage regulation issues. Using larger conductor sizes in distribution feeders reduces resistance and voltage drops.
Load balancing across multiple phases and feeders prevents excessive voltage drop on individual phases or circuits.
Relationship Between Voltage Regulation and Efficiency
While voltage regulation and efficiency are distinct transformer performance parameters, they exhibit important interrelationships that influence transformer selection and operation.
Transformers with lower voltage regulation typically have lower internal impedance, which generally correlates with reduced copper losses and improved efficiency under load. However, this relationship is not absolute, as efficiency also depends on core losses, which are independent of load current.
Voltage Regulation Calculator
This calculator simplifies voltage regulation analysis by offering two calculation approaches: use the voltage-based method when you have actual measurements of no-load and full-load voltages, or employ the parameter-based method to explore how transformer resistance, reactance, and load power factor influence regulation.
The calculator not only computes the regulation percentage but also provides color-coded interpretations ranging from excellent (0-2%) to poor (above 6%), along with the mathematical formulas used, making it an invaluable educational and practical tool for electrical engineering students and professionals alike.
⚡ Transformer Voltage Regulation Calculator
Calculate transformer voltage regulation using voltages or parameters. Results explain performance instantly!
Using No-load & Full-load Voltages
Conclusion
Voltage regulation stands as a fundamental performance parameter defining a transformer’s ability to maintain stable output voltage under varying load conditions. Knowing the voltage regulation principles, mathematical relationships, influencing factors, and practical implications enables electrical engineers to design robust power systems, select appropriate transformers, and implement effective voltage control strategies