Transformer impedance is fundamental for the design, operation, and protection of power systems. This parameter influences voltage regulation, fault current levels, parallel operation, and overall system stability.
What is Transformer Impedance?
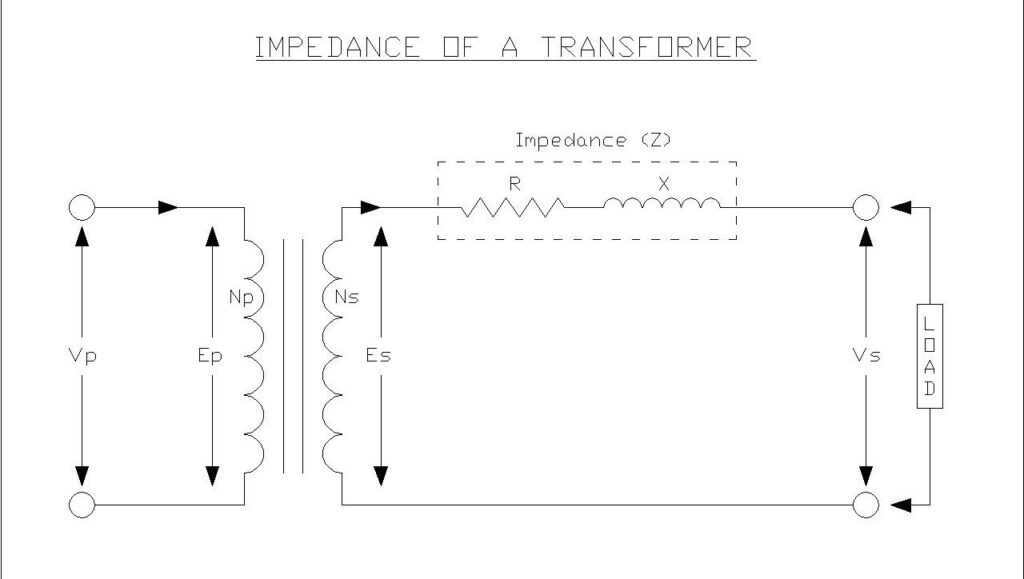
Transformer impedance represents the total opposition that a transformer offers to alternating current flow through its windings. Unlike a simple resistance, transformer impedance is a complex quantity comprising both resistive and reactive components, mathematically expressed as the vector sum of winding resistance and leakage reactance.
In practical transformers, both the primary and secondary windings possess finite resistance due to the copper or aluminum conductors used in their construction. Additionally, not all magnetic flux generated by one winding successfully links with the other winding—some flux “leaks” through paths outside the magnetic core, creating leakage reactance. This leakage flux is inherent to transformer operation.
When an AC voltage is applied to a transformer’s primary winding, the impedance opposes current flow, resulting in a voltage drop across the windings. The magnitude of this voltage drop directly correlates with the transformer’s impedance value, making it a crucial parameter for predicting transformer performance under various loading conditions.
Percentage Impedance

The percentage impedance (also called impedance voltage) is perhaps the most practical way to express transformer impedance, as it appears on every transformer nameplate. Percentage Impedance represents the percentage of rated voltage required to circulate rated full-load current through one winding when the other winding is short-circuited at rated frequency.
For example, consider a transformer with a 5% impedance rating and a primary voltage of 11,000V. When the secondary winding is short-circuited, applying just 5% of the rated voltage (550V) to the primary winding will cause rated full-load current to flow through both windings. Conversely, if the full 11,000V were applied under short-circuit conditions, the current would reach approximately 20 times the rated current (100% ÷ 5% = 20).
The mathematical definition of percentage impedance is given by:
\( \%Z = \left( \frac{V_{sc}}{V_{rated}} \right) \times 100 \)
where \(V_{sc}\) represents the voltage applied during the short-circuit test that produces rated current, and \(V_{rated}\) is the transformer’s rated primary voltage.
Components of Transformer Impedance
Transformer impedance consists of two fundamental components that contribute to the total opposition to current flow as discussed above:
Winding Resistance
The resistance component results from the physical resistance of the copper or aluminum conductors used in both primary and secondary windings. This resistance causes \(I^2R\) losses (copper losses) during operation, which appears as heat dissipation and reduce transformer efficiency. The total equivalent resistance referred to either the primary or secondary side represents the sum of both winding resistances, appropriately transformed by the turns ratio.
Leakage Reactance
The reactance component arises from leakage flux—the portion of magnetic flux that links only one winding rather than both. In an ideal transformer, all flux generated by the primary winding would pass through the core and link perfectly with the secondary winding. In reality, some flux takes alternative paths through air, insulating oil, and structural materials.
This leakage flux induces self-reactance in each winding, represented as leakage reactance in the equivalent circuit. The leakage reactance depends on several design factors including winding geometry, spacing between windings, number of turns, core window size, and insulation thickness.
The total impedance is the vector sum of resistance and reactance:
\( Z_{eq} = \sqrt{R_{eq}^2 + X_{eq}^2} \)
where \(R_{eq}\) is the equivalent resistance and X_{eq} is the equivalent leakage reactance, both referred to the same side of the Transformer.
Typical Impedance Values and Standards
Transformer impedance values are not arbitrary—they follow well-established standards and typical ranges based on transformer size, voltage class, and application. International standards including IEEE C57.12.34, IEC 60076, and CSA C227.4 specify recommended impedance ranges for different transformer ratings.
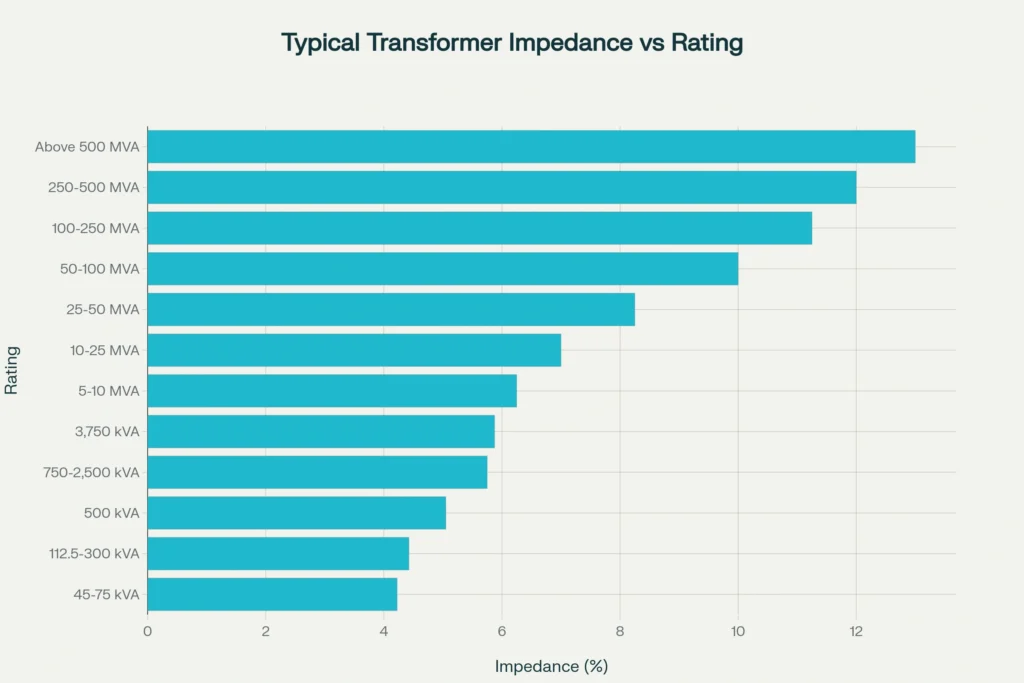
Distribution transformers (below 1 MVA) typically exhibit impedance values ranging from 4% to 6%. These relatively low impedance values help minimize voltage drops during normal operation, ensuring better voltage regulation for consumers. As transformer capacity increases, so does the typical impedance percentage—medium power transformers (1-10 MVA) generally have impedances between 5.75% and 7.5%.
Large power transformers used in transmission networks exhibits even higher impedance values. Substations transformers in the 10-100 MVA range typically exhibit 7% to 11% impedance, while extra-high voltage (EHV) transmission transformers above 100 MVA commonly have impedances ranging from 10% to 14%. This progressive increase serves a crucial protective function by limiting the massive fault currents that could otherwise flow in high-capacity systems.
Standards typically allow a tolerance of ±7.5% to ±10% from the specified impedance value after manufacturing. For instance, a 33 MVA, 132/6.6 kV transformer with a specified 13% impedance should measure between 12.87% and 13.13% during factory acceptance testing.
Measurement of Transformer Impedance: The Short-Circuit Test
The short-circuit test (also called the impedance test or load loss test) represents the standard method for determining a transformer’s impedance. This carefully controlled procedure measures impedance without risking transformer damage from excessive current.
Test Procedure
The short-circuit test follows a systematic procedure:
- Short-circuit the secondary winding using a low-resistance conductor (typically the low-voltage winding for safety reasons)
- Apply voltage to the primary winding starting from zero, using a variable voltage source (variac)
- Gradually increase the applied voltage while monitoring the secondary current
- Record readings when the secondary current reaches the rated full-load value
- Measure and document the applied voltage, current, and power consumption at this operating point
The voltage required to circulate rated current under these short-circuit conditions represents the impedance voltage. When this voltage is expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage, it directly equals the percentage impedance.
Calculations and Parameters
From the short-circuit test measurements, several critical parameters can be calculated:
Equivalent impedance:
\( Z_{01} = \frac{V_{sc}}{I_{rated}} \)
Equivalent resistance (from wattmeter reading):
\( R_{01} = \frac{W_{sc}}{I_{rated}^2} \)
Equivalent reactance:
\( X_{01} = \sqrt{Z_{01}^2 – R_{01}^2} \)
where \(W_{sc}\) represents the power measured during the short-circuit test, primarily consisting of copper losses at full load.
The test is typically performed on the high-voltage side with the low-voltage side short-circuited, as this arrangement requires lower test voltages and is safer to conduct. Because the applied voltage is only a small percentage of rated voltage (typically 4-15%), core losses remain negligible, and the measured power essentially equals the copper losses at full load.
The Role of Impedance in Transformer Performance
Voltage Regulation
Voltage regulation describes how transformer secondary voltage changes between no-load and full-load conditions for a constant primary voltage. Impedance directly determines voltage regulation—higher impedance produces greater voltage drops under load, resulting in poorer regulation.
The voltage regulation can be calculated using:
\( \%Regulation = \frac{I_S(R\cos\phi \pm X\sin\phi)}{V_{no-load}} \times 100\% \)
where \(I_s\) is the secondary current, \(R\) and \(X\) are the equivalent resistance and reactance, and \(\phi\) is the power factor angle. The \(\pm\) sign depends on whether the load has a lagging (inductive) or leading (capacitive) power factor.
Short-Circuit Current Limitation
One of the most critical protective functions of transformer impedance is limiting fault currents during short-circuit conditions. When a fault occurs on the secondary side, the transformer’s impedance restricts the magnitude of fault current that can flow.
The short-circuit current can be approximated by:
\( I_{sc} = \frac{I_{rated} \times 100}{\%Z} \)
A transformer with 5% impedance will produce a short-circuit current approximately 20 times its rated current, while a 10% impedance transformer limits this to 10 times rated current. Higher impedance transformers provide better protection against short-circuit damage but at the cost of increased voltage drop during normal operation. This protective characteristic becomes increasingly important in high-capacity systems where fault currents can reach destructive levels.
System Efficiency
Transformer impedance affects system efficiency through the voltage drops and losses it creates. The resistive component causes direct power loss proportional to the square of the load current, while the reactive component influences the voltage drop and maximum flux density in the core.
Lower impedance transformers generally exhibit better efficiency under normal loading conditions because they produce smaller voltage drops and allow more effective power transfer to the load. However, this advantage must be weighed against the increased short-circuit current stress and the need for more robust downstream equipment capable of withstanding higher fault levels.
High Impedance vs. Low Impedance Transformers
High Impedance Transformers
Advantages:
- Superior short-circuit protection through significant fault current limitation
- Reduced stress on system insulation and equipment during faults
- Better suited for stiff power systems with high available fault currents
- Enhanced protection against poor power factor conditions
Disadvantages:
- Increased voltage drop under load, resulting in poorer voltage regulation
- Higher voltage required to produce full-load current
- Reduced efficiency due to greater impedance losses
- Potential for voltage instability in weak systems
High impedance transformers find application in situations where limiting fault currents is paramount, such as industrial facilities with extensive downstream equipment or systems where existing switchgear has limited breaking capacity.
Low Impedance Transformers
Advantages:
- Excellent voltage regulation with minimal voltage drop under varying loads
- Higher efficiency during normal operation
- Better performance in weak systems or at the remote ends of long distribution lines
- Improved ability to start large motors without excessive voltage sag
Disadvantages:
- Higher short-circuit currents requiring more robust and expensive protective equipment
- Increased stress on transformer insulation during fault conditions
- Greater potential for damage during short-circuit events
Low impedance transformers (typically 2-4%) are often specified for distribution systems serving remote loads where voltage regulation is critical, or where the system impedance is already high enough to naturally limit fault currents.
Parallel Operation and Impedance Matching
Parallel operation of transformers provides various advantages including load sharing, improved efficiency, redundancy, and flexible capacity management.
Requirements for Parallel Operation
For transformers to share load properly when operated in parallel, several conditions must be satisfied:
- Identical voltage ratios to prevent circulating currents under no-load conditions
- Same percentage impedance on their respective MVA ratings
- Identical impedance angle (X/R ratio) to ensure proper real and reactive power sharing
- Same phase displacement and vector group
- Matched polarity across all terminals
Impact of Impedance Mismatch
The percentage impedance requirement is particularly critical. Load sharing between paralleled transformers is inversely proportional to their impedances. When transformers with different percentage impedances operate in parallel, the transformer with lower impedance carries a disproportionately higher share of the total load.
Consider two 25 MVA transformers connected in parallel, one with 9% impedance and the other with 11% impedance. When supplying a combined 40 MW load, the 9% impedance transformer will carry approximately 88.6% of its rating while the 11% impedance transformer only carries 72.5% of its rating. This unequal load sharing prevents full utilization of installed capacity and can lead to overloading of the lower-impedance unit.
For satisfactory parallel operation, circulating current should not exceed 10% of the full-load rated current of the smaller unit. Standards typically allow impedance tolerances of ±7.5% to ±10%, meaning transformers with nominally identical impedances may still exhibit slight differences that affect load sharing.
Parallel Operation Benefits and Challenges
When properly matched, paralleled transformers offer significant benefits:
- Load sharing proportional to transformer ratings
- Improved overall efficiency by optimizing loading across units
- Redundancy for maintenance and emergency conditions
- Flexible capacity expansion without replacing existing equipment
However, parallel operation also introduces challenges:
- Increased system fault levels due to reduced combined impedance
- Higher circuit breaker and bus ratings required
- Complex protection coordination requirements
- Sensitivity to tap changer position mismatches
Transformer Impedance in Power System Protection
Transformer impedance plays a vital role in power system protection schemes, influencing both fault level calculations and protection device coordination.
Fault Level Calculations
Accurate knowledge of transformer impedance is essential for calculating available fault currents at various points in the power system. The transformer impedance forms part of the total system impedance that limits fault current magnitude.
For a typical fault calculation, the infinite bus method uses transformer impedance as:
\( I_{fault} = \frac{I_{rated} \times 100}{\%Z} \times \frac{V_{actual}}{V_{rated}} \)
Protection Schemes
Several protection schemes rely on transformer impedance characteristics:
Differential protection compares currents entering and leaving the transformer, accounting for the impedance and turns ratio to detect internal faults. The impedance influences the sensitivity settings and restraint characteristics of differential relays.
Restricted earth fault protection provides sensitive ground fault detection for grounded wye-connected windings, with settings influenced by the transformer’s zero-sequence impedance. This impedance differs significantly from positive-sequence impedance and depends on core construction and winding connections.
Distance protection for transformer-feeder arrangements uses impedance measurement principles, with the protection zone set to reach partway into the transformer impedance. Proper zone setting requires accurate impedance data to ensure adequate protection coverage without unwanted operations.
Overcurrent protection settings must account for transformer impedance to coordinate properly with upstream and downstream devices while providing adequate sensitivity for internal faults. The impedance determines the magnitude of fault current available to operate protective relays.
Zero-Sequence Impedance
Zero-sequence impedance represents a specialized impedance measurement critical for analyzing unbalanced faults, particularly line-to-ground faults. Unlike positive- and negative-sequence impedances which are typically equal, zero-sequence impedance can differ dramatically depending on transformer winding connections and core construction.
Measurement and Significance
Zero-sequence impedance is measured using a single-phase test where all three phase terminals are connected together and energized relative to a neutral point. The voltage is increased until rated current flows, similar to the positive-sequence short-circuit test.
For grounded wye-grounded wye transformers with three-limb core construction, zero-sequence flux must find return paths through tank walls, oil, and air rather than through the core iron. This results in complex zero-sequence behavior requiring multiple tests to characterize fully. Four separate tests may be necessary to determine all parameters of the equivalent T-model used for system studies.
The zero-sequence impedance strongly influences ground fault current magnitudes and the effectiveness of ground fault protection schemes. Accurate zero-sequence data is essential for protective relay settings, particularly for restricted earth fault and differential protection.
Transformer Connection Effects
Zero-sequence impedance behavior varies dramatically with winding connections:
- Delta windings provide a closed path for zero-sequence currents, trapping them and preventing propagation to other windings
- Ungrounded wye windings offer infinite zero-sequence impedance as no path exists for zero-sequence current flow
- Grounded wye windings allow zero-sequence current flow, with impedance depending on grounding method and core design
- Three-limb cores typically exhibit lower zero-sequence impedance than five-limb cores due to magnetic flux paths
Transformer Impedance Calculator
Transformer Impedance Calculator
Calculate impedance, fault current, and percentage impedance with precision
Formula: Z = V / I
Calculate impedance from voltage and current values
Educational tool for electrical engineering calculations. Always verify results with professional standards.
Quiz on Transformer Impedance
Transformer Impedance Quiz
Test your knowledge of transformer impedance concepts and calculations
Ready to Test Your Knowledge?
This comprehensive quiz covers transformer impedance concepts from basic fundamentals to advanced applications used in electrical engineering.
Based on your performance, here are some areas to focus on:
Conclusion
Transformer impedance represents a fundamental parameter that profoundly influences power system design, operation, and protection. This complex quantity, comprising both resistive and reactive components, determines voltage regulation, limits fault currents, enables parallel operation, and affects overall system efficiency.
Transformer impedance concepts is essential for electrical engineers working with power systems. In designing new installations, analyzing existing networks, or troubleshooting operational issues, a thorough understanding of how transformer impedance affects system behavior enables more effective engineering decisions and more reliable power system operation.