Electrical safety is one of the most important aspects of any electrical installation. Whether it is a home, office, or industrial setup, protecting people from electric shocks is essential. This is where Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) plays an important role.
RCCB is a life-saving device that protects humans from electric shocks and prevents electrical fires.
In this technical guide, we will learn everything about RCCB including working principle, components, types, technical specifications, advantages, disadvantages and applications.
1. What is RCCB?
RCCB is an electrical safety device that automatically disconnects the circuit when it detects any leakage of current. It is also known as RCD (Residual Current Device) in some countries.

The main purpose of RCCB is to protect people from electric shock caused by direct or indirect contact with live parts. It continuously monitors the flow of current in the circuit and trips immediately when there is an imbalance.
RCCB detects earth fault currents and leakage currents with high accuracy. However, it does not provide protection against short circuits or overload conditions. This is why RCCB is always used along with MCB for complete circuit protection.
In many countries, installing RCCB is mandatory for residential electrical installations. The device operates very quickly typically within 30 milliseconds. This is fast enough to prevent serious injury.
2. Working Principle of RCCB
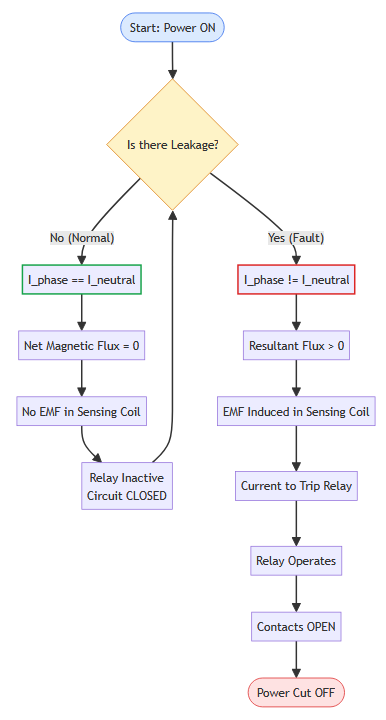
The working principle of RCCB is based on Kirchhoff’s Current Law. According to this law, the current entering a circuit must be equal to the current leaving the circuit.
In a healthy circuit, the current flowing through the phase wire is exactly equal to the current returning through the neutral wire. The RCCB continuously compares these two currents using a core balance current transformer (CBCT).
Both phase and neutral wires pass through this transformer. Under normal conditions, the magnetic flux produced by the phase wire is equal and opposite to the flux produced by the neutral wire. These two fluxes cancel each other resulting in zero net flux in the core.
When a leakage occurs, some current flows to the earth instead of returning through the neutral wire. This creates a difference between the phase current and neutral current. The difference in current causes an unbalanced magnetic flux in the transformer core. This unbalanced flux induces a small current in the sensing coil, which activates the trip mechanism. The RCCB immediately disconnects the circuit and prevents electric shock.
3. Circuit Diagram of RCCB
The figure below shows a 2 Pole Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) circuit. Let me explain how it works based on the image:.
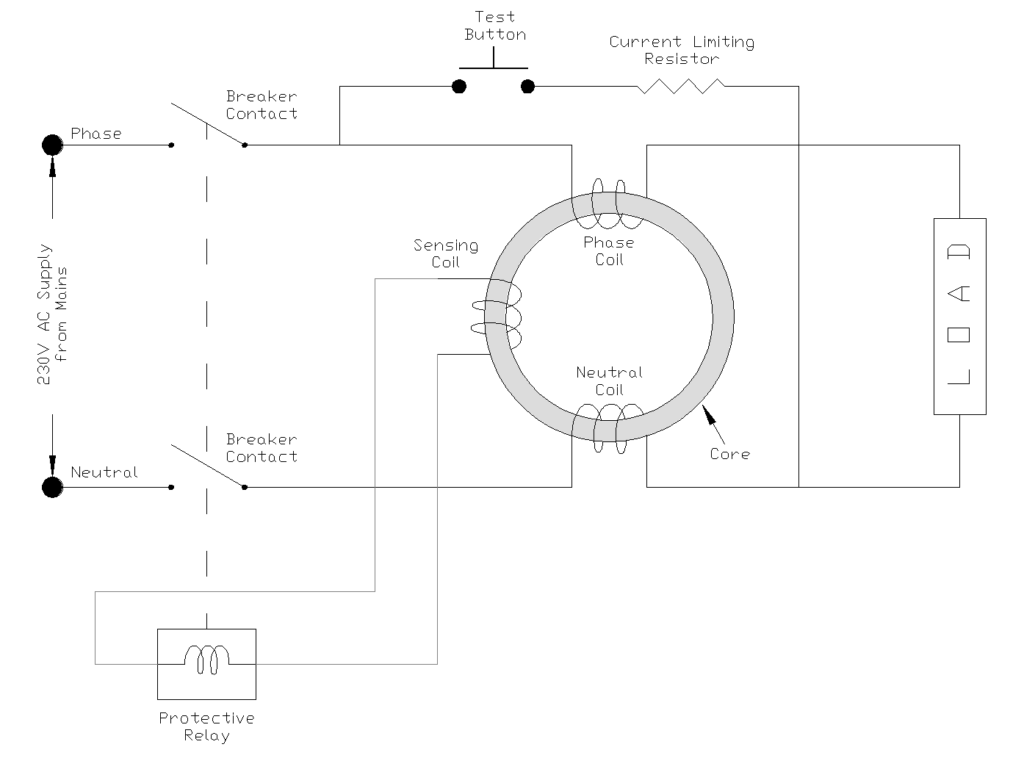
3.1 Main Components:
- Power Supply: 230V AC supply from mains with Phase and Neutral lines
- Breaker Contacts: Mechanical switches that can interrupt the circuit
- Test Button: Manual test mechanism with a current limiting resistor
- Toroidal Core Assembly: The heart of the device containing three coils:
- Phase Coil: Carries the live current
- Neutral Coil: Carries the return current
- Sensing Coil: Detects any imbalance between phase and neutral
- Protective Relay: Trip mechanism that opens the breaker contacts
- Load: The electrical appliance or circuit being protected
3.2 Normal Operation
Under normal conditions, the current flowing through the phase coil equals the current returning through the neutral coil. These currents create equal and opposite magnetic fields in the toroidal core that cancel each other out, so no voltage is induced in the sensing coil.

3.3 Ground Fault Condition
If current leaks to ground (like through a person touching a live wire), the current in the phase coil no longer equals the neutral coil current. This imbalance creates a net magnetic field in the core.
The sensing coil detects this magnetic imbalance and induces a voltage that energizes the protective relay. The relay then trips open the breaker contacts, disconnecting power to the load within milliseconds.
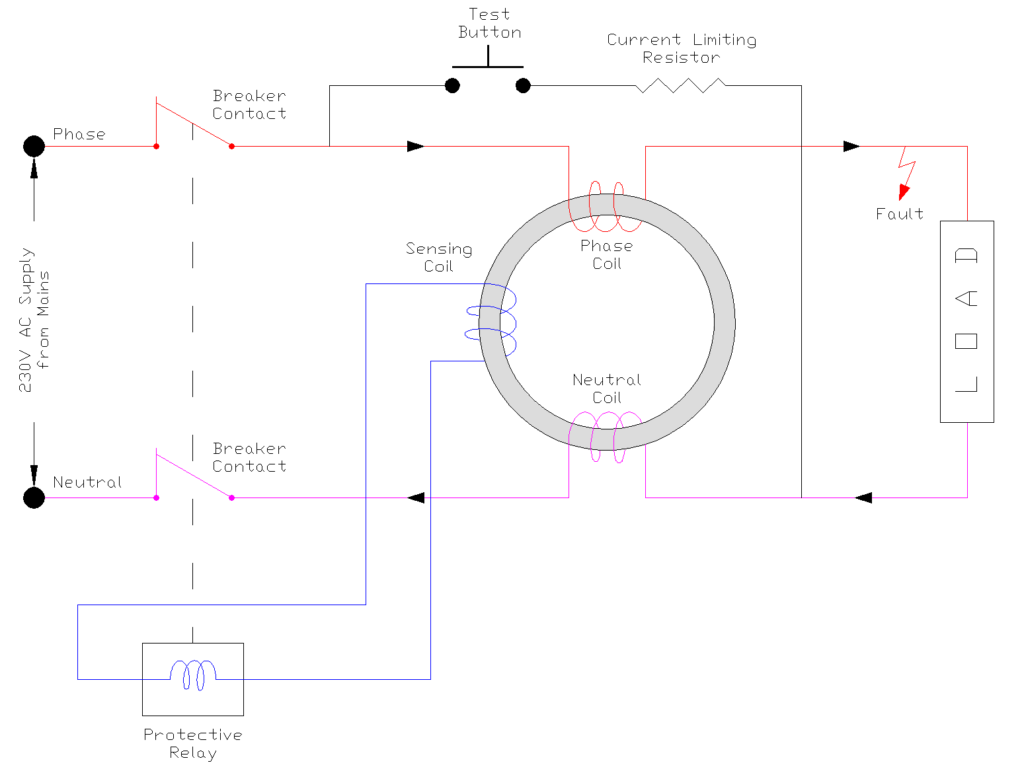
Test Function: The test button allows you to verify the RCCB is functioning by intentionally creating an imbalance that should trip the device.
4. Types of RCCB
RCCBs are available in different types based on poles and sensitivity ratings.
4.1 Based on Number of Poles
Two-Pole RCCB is used in single-phase electrical supply systems. It has one phase and one neutral connection. This type is suitable for homes and small offices and is the most commonly used configuration in residential installations.
Four-Pole RCCB is used in three-phase electrical supply systems. It has three phase connections and one neutral connection. This type is suitable for industrial and commercial installations where three-phase power is used. It protects all three phases simultaneously.
4.2 Based on Sensitivity Rating
Different sensitivity ratings are used for different applications.
The 10mA RCCB offers high sensitivity and is typically used for medical equipment. The 30mA RCCB is the standard choice for personal protection in homes and is most widely used.
The 100mA RCCB is primarily used for fire protection purposes. The 300mA and 500mA RCCBs are used for main distribution boards and large commercial installations respectively.
5. Technical Specifications of RCCB
When selecting an RCCB for any installation, you must understand its technical specifications. These specifications determine whether the device is suitable for your application.
Important specifications to consider:
- Rated Current: Available in 16A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 63A, 80A, and 100A
- Rated Sensitivity: Common values are 30mA, 100mA, and 300mA
- Rated Voltage: Usually 230V for single-phase and 415V for three-phase
- Number of Poles: 2-pole or 4-pole options
- Breaking Capacity: Typically 3000A to 10000A
- Tripping Time: Usually less than 40 milliseconds
- Operating Temperature: Generally -5°C to +40°C
6. Standard RCCB Rating Chart
6.1 Single Phase (2-Pole) – Residential & Small Office
Used for standard 230V/240V supplies.
| Current Rating (In) | Sensitivity (IΔn) | Typical Application | Recommended Wire Size (Cu) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16A / 20A | 10mA / 30mA | Specific wet areas, Jacuzzis, Medical equipment | 2.5 mm² |
| 25A | 30mA | Small apartments, Lighting circuits, Outbuildings | 4.0 mm² |
| 32A | 30mA | Standard house ring mains, Dedicated AC units | 6.0 mm² |
| 40A | 30mA | Most Common Standard House Main Switch | 10.0 mm² |
| 63A | 30mA / 100mA | Large homes, Electric Showers, EV Chargers | 16.0 mm² |
| 80A / 100A | 100mA / 300mA | Main distribution for very large residences | 25.0 mm² – 35.0 mm² |
6.2 Three Phase (4-Pole) – Commercial & Industrial
Used for 400V/415V supplies.
| Current Rating (In) | Sensitivity (IΔn) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| 25A | 30mA | Small 3-phase motors, pumps, HVAC controls |
| 40A | 30mA / 100mA | Small workshops, Commercial distribution boards |
| 63A | 30mA / 100mA / 300mA | Office buildings, Industrial machinery, Elevators |
| 100A | 100mA / 300mA | Main building distribution, Factory mains |
| 125A+ | 300mA / 500mA | Heavy industrial Mains (Fire protection focus) |
7. Advantages of RCCB
RCCB offers many benefits that make it an essential device in electrical installations. It provides reliable protection against various electrical hazards.
The primary advantage of RCCB is its excellent protection against electric shock. It detects earth leakage faults effectively and operates very quickly to minimize injury. RCCB also prevents electrical fires caused by leakage currents flowing through unintended paths.
The device is easy to install and maintain. It comes with a test button for regular testing. RCCBs are available in various ratings for different applications, making them versatile for all types of installations. They have a long service life with minimal maintenance requirements.
Another significant advantage is that RCCB operates automatically without human intervention. Unlike fuses, RCCBs are reusable after tripping and do not require replacement of any component.
8. Disadvantages of RCCB
While RCCB is very useful, it also has some limitations.
The main limitation of RCCB is that it does not protect against short circuits or overload conditions. It can only detect earth leakage and residual currents. This is why RCCB must always be used in combination with MCB for complete protection.
RCCB may cause nuisance tripping in some conditions, especially in installations with long cable runs or high humidity. It requires proper earthing for effective operation. Standard AC type RCCBs cannot detect DC leakage currents which may be present in installations with electronic equipment.
The device is more expensive than standard circuit breakers. It may not work properly if neutral and earth are mixed up in the installation. Regular periodic testing is required to ensure proper operation.
9. Applications of RCCB
RCCB is used in various places where protection against electric shock and earth leakage is required. Its application depends on the sensitivity rating and current capacity.
In residential buildings and apartments, RCCB is installed to protect family members from electric shock. The 30mA sensitivity RCCB is most commonly used for this purpose. Commercial offices, shops, hotels, and restaurants also use RCCB for safety of employees and customers.
Industrial installations use higher rated RCCBs for fire protection and equipment safety. Special attention is given to wet areas like swimming pools and bathrooms, where the risk of electric shock is higher. Outdoor electrical installations also require RCCB because of exposure to weather conditions.
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use high-sensitivity RCCBs to protect patients and medical equipment. Schools, educational institutions, construction sites, and agricultural installations are other common application areas.
10. Difference Between RCCB and MCB
Many students get confused between RCCB and MCB. Both are protective devices but serve different purposes.
MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker. It protects against overload currents and short circuit currents. MCB operates based on thermal and magnetic principles. When current exceeds the rated value, the thermal element heats up and trips the breaker. For short circuits, the magnetic element provides instantaneous tripping. MCB is available in different trip curves such as B, C, and D for different applications. However, MCB does not detect earth leakage.
RCCB protects against earth leakage currents and electric shock. It operates based on the current difference principle. When the current flowing in phase and neutral wires is not equal, RCCB trips the circuit. However, RCCB does not protect against overload or short circuit.
For complete protection, both RCCB and MCB should be installed together. The MCB protects the equipment and wiring, while the RCCB protects human life.
11. How to Select the Right RCCB
Selecting the correct RCCB is important for effective protection. Wrong selection can lead to nuisance tripping or inadequate protection.
First, determine whether you need a 2-pole or 4-pole RCCB. For single-phase supply, choose 2-pole RCCB. For three-phase supply, choose 4-pole RCCB.
Next, select the appropriate sensitivity rating. For personal protection in homes and offices, 30mA sensitivity is recommended. For fire protection in commercial and industrial installations, 100mA or higher sensitivity is suitable.
The rated current of RCCB should be equal to or greater than the circuit load current. Ensure that the RCCB voltage rating matches your supply voltage. Consider the type of load connected to the circuit. If electronic equipment with DC components is present, consider using AC/DC sensitive type RCCB.
Check the breaking capacity to ensure it is suitable for your installation. Always buy RCCB from reputed brands to ensure reliability and safety.
12. Installation Guidelines for RCCB
The RCCB should be installed after the main MCB or isolator in the distribution board. Connect the phase wire to the terminal marked “L” and the neutral wire to the terminal marked “N”. Always follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram strictly.
Proper earthing of the installation is essential for RCCB to work effectively. Do not mix neutral wires of different circuits downstream of the RCCB. Never connect neutral to earth after the RCCB, as this will cause immediate tripping.
Mount the RCCB in a vertical position as recommended by the manufacturer. Keep the RCCB accessible for testing and operation. After installation, always test the RCCB using the test button to verify proper operation before energizing the circuit.
13. Testing and Maintenance of RCCB
To test the RCCB, simply press the test button provided on the device. The RCCB should trip immediately when the test button is pressed. After testing, reset the RCCB by pushing the operating knob up. If the RCCB does not trip when the test button is pressed, it indicates a fault and the device needs replacement. Testing should be performed at least once every month.
For maintenance, keep the RCCB clean and dust-free. Check terminal connections periodically to ensure they are tight. Look for any signs of burning, discoloration, or damage. If the RCCB trips frequently without any apparent reason, investigate the cause or replace the device.
Do not attempt to repair a faulty RCCB yourself. Always replace it with a new one. As a general guideline, replace RCCB after 10-15 years of service even if it appears to be working properly.
14. Conclusion
RCCB is an essential electrical safety device that protects human life from electric shock. It works by detecting the difference between phase and neutral currents and trips the circuit when leakage is detected.
Every modern electrical installation should have RCCB installed for adequate protection. While RCCB does not protect against short circuits and overloads, combining it with MCB provides complete protection for both equipment and human life.
15. Frequently Asked Questions About RCCB
RCCB can detect leakage even without proper earthing when current flows through the human body to earth. However, proper earthing improves the effectiveness of protection and ensures faster tripping in case of insulation failure.
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is an older technology that detects voltage on the earth conductor. RCCB is a newer and more reliable technology that detects current imbalance. RCCB is preferred over ELCB in modern installations.
No, RCCB cannot protect against short circuits. For complete protection, use RCCB along with MCB. The MCB will handle short circuit and overload protection while RCCB handles earth leakage protection.
RCBO stands for Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection. It combines the functions of both RCCB and MCB in a single device, providing protection against earth leakage, overload, and short circuit.